Store app and user states
- How-to
- 6 minutes
The state service is your best option if your app needs internal global states or user-specific states. One common usage is caching the result of an app function.
This guide explains how to create, update, and delete app states and user app states. The @dynatrace-sdk/react-hooks package provides hooks so you can do all these operations.
When you run your app on your local development server, the states are confined to the local development's scope. So, you won't be in danger of overriding the deployed app's states during development.
States are persistent across updates of an app. So, you must migrate any states needed for a new app version in the app's code.
Set a state by key
To set the app or user app state, you can use the setAppState or setUserAppState hooks from the @dynatrace-sdk/react-hooks package. These hooks provide an execute function to create a new state, and additional fields about the loading status, errors, and response. These fields are common to all the app and user app state hooks. The example below shows how to create an app state for storing weather information:
Add a version field to your state to make future migrations easier.
import React from 'react';
import { useSetAppState } from '@dynatrace-sdk/react-hooks';
import { Button } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/buttons';
import { Page } from '@dynatrace/strato-components-preview/layouts';
export const App = () => {
const { execute } = useSetAppState();
const handleClick = () => {
execute({
key: 'weather',
body: {
value: JSON.stringify({
version: '1',
timestamp: Date.now(),
weather: { city: 'Vienna', temperature: 23, unit: 'celsius' },
}),
validUntilTime: 'now+1d',
},
});
};
return (
<Page>
<Button onClick={handleClick}>Set app state</Button>
</Page>
);
};
This operation requires the following scopes:
state:app-states:writestate:user-app-states:write
State validity
By default, app states and user app states don't expire. To define states that are only valid for a certain period, you can provide an optional validUntilTime, which ensures the presence of the state until the time expires. States are deleted after their validUntilTime elapses.
You can provide the validUntilTime in two ways:
- A relative time format such as
now+1mornow+30d:- The format is
now+NUwhereNis the amount of time,Uis the unit of time (s - seconds, m - minutes, h - hours, d - days).
- The format is
- A timestamp in ISO 8601 format.
For both types, you can specify a timeframe of 1 minute to 90 days.
Every app state hook has an equivalent user app state hook. For instance, the equivalent of useSetAppState is useSetUserAppState. All the examples in this guide use the app state hooks.
Get a state by key
To fetch a previously stored state, you can use the useAppState and useUserAppState hooks and pass the key of the write operation as the parameter. The validUntilTime follows an ISO 8601 syntax. The hooks also provide a function to refetch the latest state. The following code fetches the state from the previous example.
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { useAppState } from '@dynatrace-sdk/react-hooks';
import { Button } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/buttons';
import { Flex } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/layouts';
import { Text } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/typography';
import { Page } from '@dynatrace/strato-components-preview/layouts';
interface Weather {
city: string;
temperature: number;
unit: string;
}
export const App = () => {
const [weather, setWeather] = useState<Weather>();
const { data, refetch } = useAppState({ key: 'weather' });
useEffect(() => {
if (data) {
setWeather(JSON.parse(data.value).weather);
}
}, [data]);
const handleClick = () => {
refetch();
};
return (
<Page>
{weather && (
<Flex>
<Text>{weather.city}</Text>
<Text>
{weather.temperature} {weather.unit}
</Text>
</Flex>
)}
<Button onClick={handleClick}>Refetch app state</Button>
</Page>
);
};
This operation requires the following scopes:
state:app-states:readstate:user-app-states:read
These operations throw an exception when the state you try to retrieve doesn't exist. If that's an expected scenario in your app, you should add some exception handling. Alternatively, you could use the useAppStates hook and filter for a specific key to get an empty array if it doesn't exist.
List all states
If your app uses dynamicaly created keys instead of a fixed set of known static keys, you can get a list of all app states or user app states with the useAppStates and useUserAppStates hooks.
By default, useAppStates and useUserAppStates only return the keys. You can request additional fields by specifying them in a comma-separated string in the addFields parameter.
import React from 'react';
import { useAppStates } from '@dynatrace-sdk/react-hooks';
import { Flex } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/layouts';
import { List, Text } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/typography';
import { Page } from '@dynatrace/strato-components-preview/layouts';
export const App = () => {
const { data } = useAppStates({
addFields: 'value,modificationInfo.lastModifiedBy,validUntilTime',
});
return (
<Page>
{data && (
<List>
{data.map((state) => (
<Flex key={state.key}>
<Text>{state.value}</Text>
<Text>{state.modificationInfo?.lastModifiedBy}</Text>
<Text>{state.validUntilTime}</Text>
</Flex>
))}
</List>
)}
</Page>
);
};
This operation requires the following scopes:
state:app-states:readstate:user-app-states:read
Filter states
The useAppStates and useUserAppStates hooks let you filter states via the filter parameter for the following fields:
key, supports operators:=,!=,contains,starts-with, andends-withmodificationInfo.lastModifiedTime, supports operators:=,!=,<,<=,>, and>=modificationInfo.lastModifiedBy, supports operators:=,!=,contains,starts-with, andends-withvalidUntilTime, supports operators:=,!=,<,<=,>, and>=
Operators contains, starts-with, and ends-with are case-insensitive. Comparisons via =, != are case-sensitive.
Conditions can be connected via and and or. Individual conditions can be negated by not.
The filter string can be up to 256 characters long. You can nest conditions (using round brackets) up to 2 levels deep.
Here are some examples of how to use filters:
const appStates = useAppStates({
filter: "modificationInfo.lastModifiedTime > '2022-07-01T00:10:05.000Z'",
});
const appStatesComplexFilter = useAppStates({
filter:
"(key starts-with 'favourite' or key starts-with 'favorite') and not(key contains 'disk' or key contains 'process')",
});
const appStatesOrEmpty = useAppStates({
filter: "key = 'might-not-exist'",
});
Delete a state by key
You can delete app states and user app states that aren't needed anymore with the useDeleteAppState and useDeleteUserAppState hooks. In addition, this will free up the equivalent of the deleted value's size in the state storage quota currently available to the app:
import React from 'react';
import { useDeleteAppState } from '@dynatrace-sdk/react-hooks';
import { Button } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/buttons';
import { Page } from '@dynatrace/strato-components-preview/layouts';
export const App = () => {
const { execute } = useDeleteAppState();
const handleClick = () => {
execute({
key: 'weather',
});
};
return (
<Page>
<Button onClick={handleClick}>Delete app state</Button>
</Page>
);
};
This operation requires the following scopes:
state:app-states:deletestate:user-app-states:delete
Delete all states
The useDeleteAppStates and useDeleteUserAppStates allow you to delete all app states and user app states to completely reset the app's states:
import React from 'react';
import { useDeleteAppStates } from '@dynatrace-sdk/react-hooks';
import { Button } from '@dynatrace/strato-components/buttons';
import { Page } from '@dynatrace/strato-components-preview/layouts';
export const App = () => {
const { execute } = useDeleteAppStates();
const handleClick = () => {
execute();
};
return (
<Page>
<Button onClick={handleClick}>Delete app states</Button>
</Page>
);
};
This operation requires the following scopes:
state:app-states:deletestate:user-app-states:delete
Reset app state
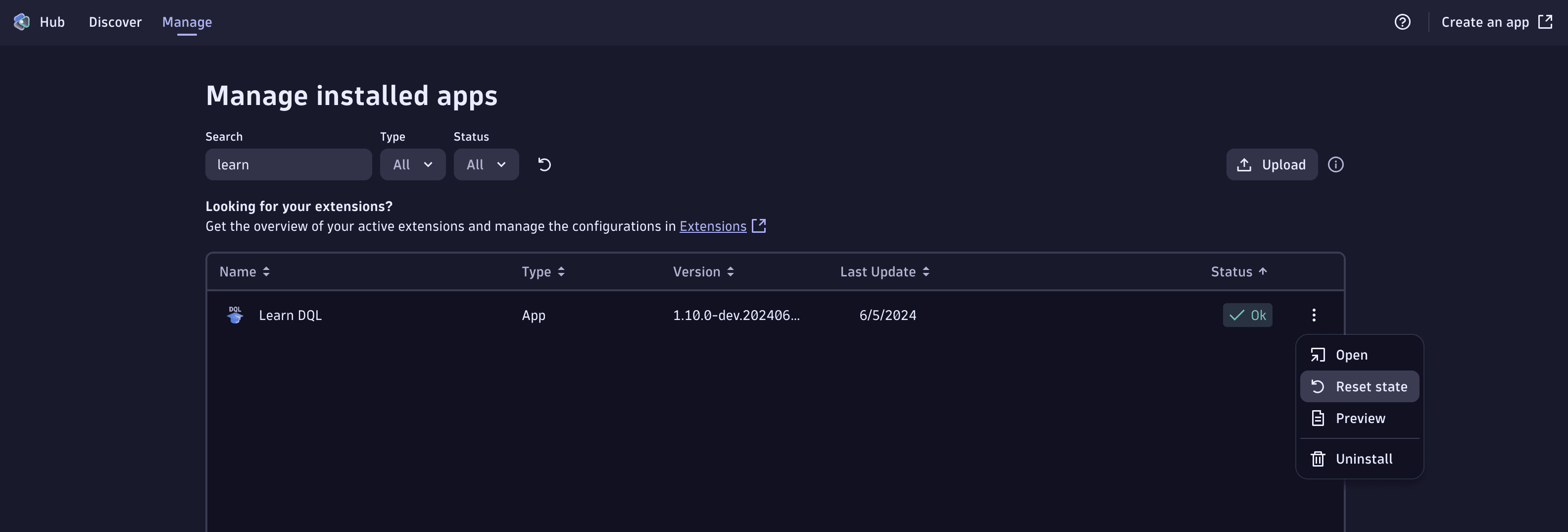
Environment admins can also manually reset an app's state. They can do so via the Hub, by following these steps:
- Open the Manage tab in the Hub app
- Find the app you want to reset the state for
- From the kebab menu on the right, click Reset state
- Select whether you want to reset your own user's state or the whole app state
- Finish by clicking Reset State, and then Confirm